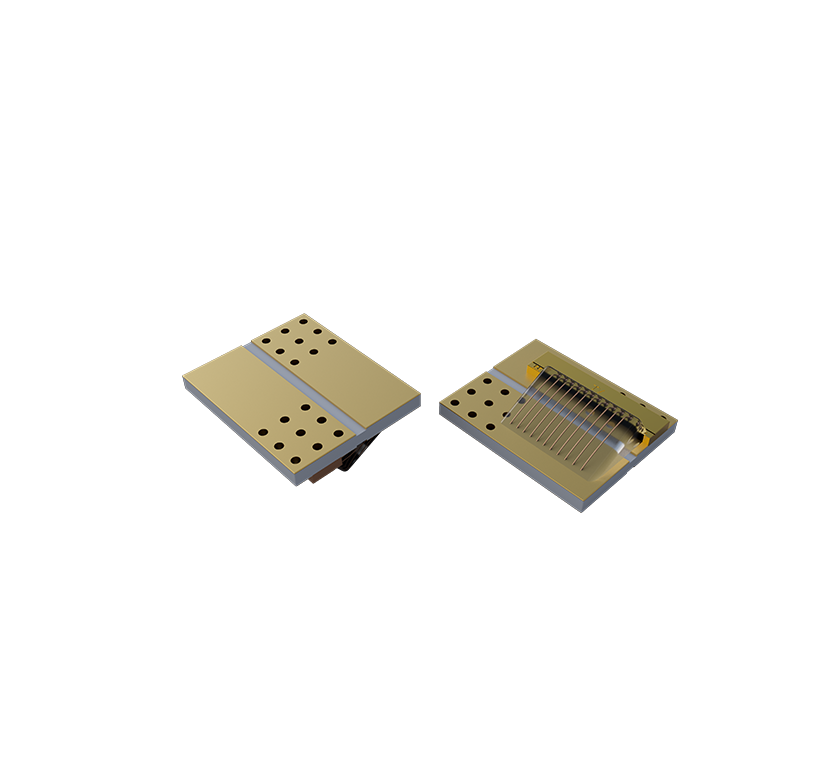
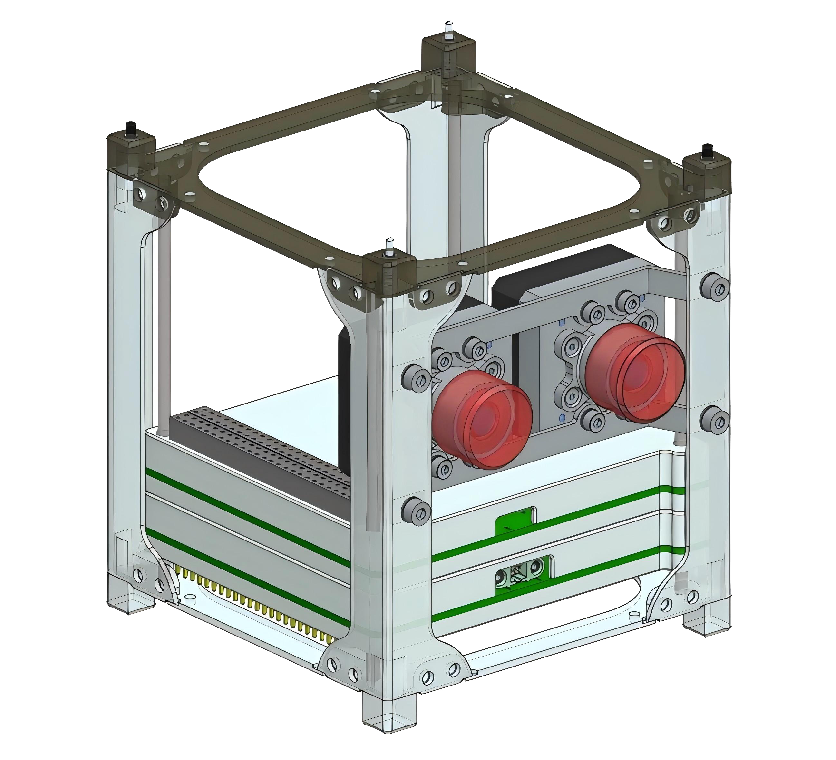
Satellite
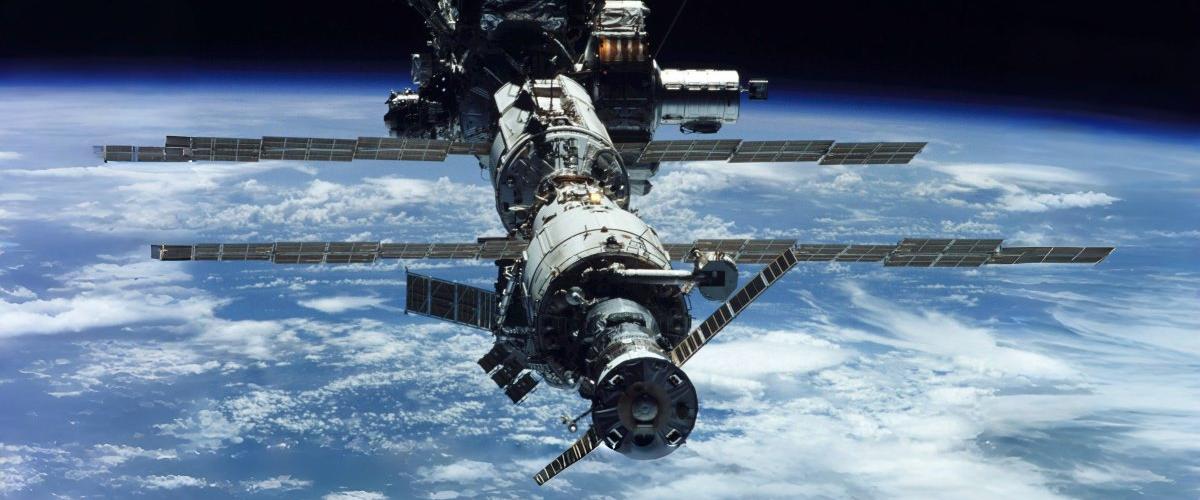
In the aerospace field, satellites are vital tools for executing a variety of critical missions. They are launched into Earth's orbit or further into space for applications such as communication, navigation, Earth observation, weather monitoring, scientific research, and military reconnaissance. Equipped with various sensors and instruments like optical cameras, radars, particle detectors, and environmental monitoring devices, satellites can gather vast amounts of data and transmit it back to ground stations. This data is essential for weather forecasting, disaster monitoring, environmental research, the Global Positioning System (GPS), and deep space exploration.
-
01
Detectable Types Are Abundant
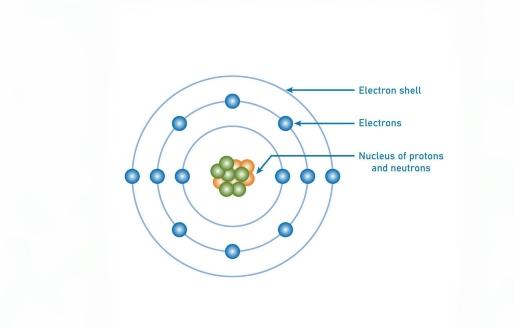
A particle detector mounted on a satellite can monitor high-energy particles in cosmic rays, solar wind, and Earth's radiation belts, including protons, electrons, neutrons, and heavy ions. It is crucial for space weather forecasting, providing early warnings of potential threats from solar storms to satellite communication and navigation systems. Additionally, by analyzing particles from the depths of the universe, scientists can study cutting-edge scientific issues such as galaxy evolution and the properties of dark matter, advancing the field of astrophysics and providing key data support for understanding the universe.

-
02
Energy Efficiency Optimization
Specialized light sources employ high-efficiency lighting technology to significantly reduce energy consumption while ensuring stable operation. These light sources can maintain high performance in extreme temperature and radiation environments, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance requirements. Their compact design saves space, and the lightweight construction reduces load, making them particularly suitable for resource-constrained spacecraft, providing reliable support for communication, remote sensing, and other missions.


-
03
Interference Resistance
Through the selection of special materials and processing techniques, the system can withstand cosmic rays and other forms of radiation, ensuring long-term stable operation. The built-in redundancy design and self-repair mechanisms further enhance the reliability and durability of the equipment, allowing the satellite to maintain high performance even under extreme space conditions.